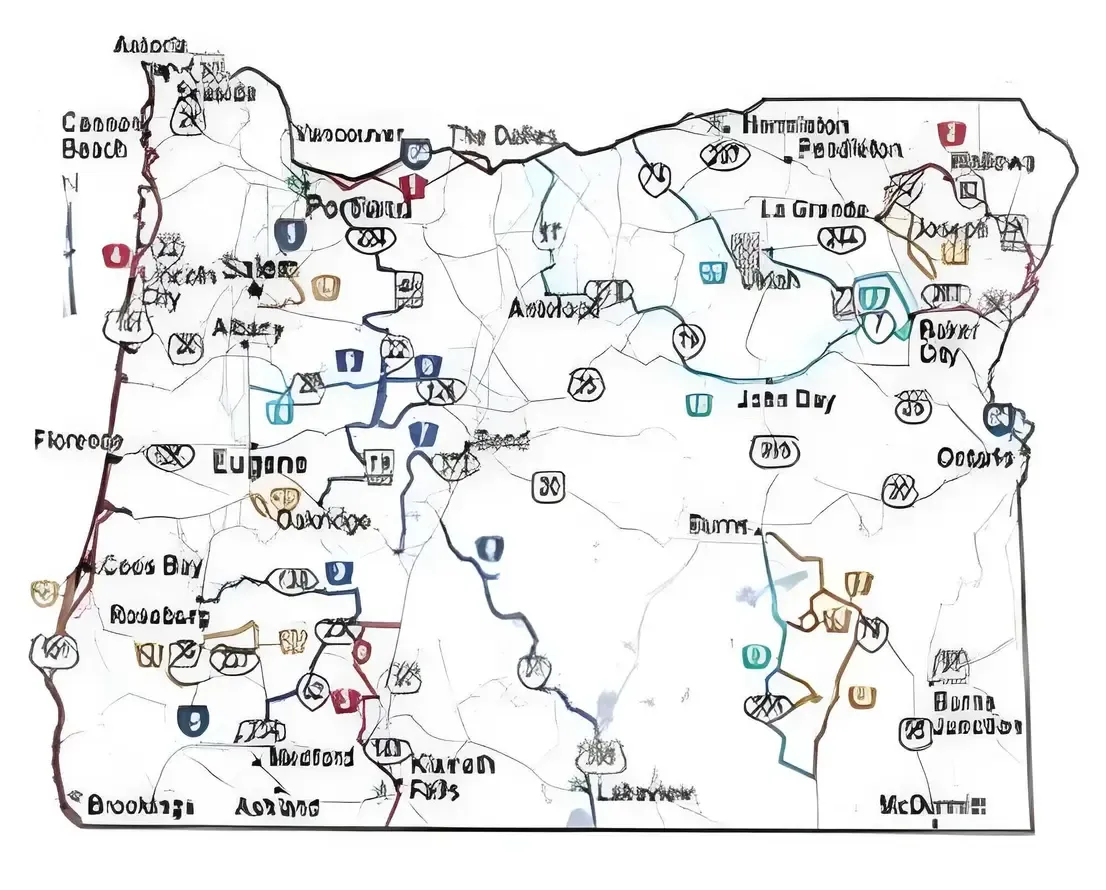
1. Interstate 5 (I-5)
-
Route: Runs north-south through Oregon, from the California border, through cities like Medford, Eugene, Salem, Portland, to the Washington border.
-
Importance for trucking:
-
Main artery for freight moving between California, Oregon, and Washington.
-
Handles the majority of long-haul trucking traffic.
-
Key for moving consumer goods, agricultural products, and manufactured goods.
-
-
Challenges:
-
Heavy congestion in Portland metro area.
-
Frequent maintenance and occasional closures due to weather or construction.
-
2. Interstate 84 (I-84)
-
Route: Runs east-west from Portland to the Idaho border, following the Columbia River Gorge in the northwest.
-
Importance for trucking:
-
Primary route for trucking to/from eastern Oregon.
-
Connects Portland with Boise, Salt Lake City, and other inland markets.
-
Supports transport of timber, agriculture, and bulk goods.
-
-
Challenges:
-
Steep grades and sharp curves in the Gorge area.
-
Winter weather hazards in eastern Oregon.
-
3. U.S. Route 101 (US-101)
-
Route: Runs along Oregon’s scenic Pacific coast, from California border to Washington border.
-
Importance for trucking:
-
Key for coastal freight, including seafood, timber, and tourism-related goods.
-
Connects small towns and ports along the coast.
-
-
Challenges:
-
Narrow lanes, limited passing zones.
-
Weather-related closures due to landslides or flooding.
-
Other Notable Routes for Trucking
-
US-26: Connects Portland to the central Oregon region. Important for timber and agricultural transport.
-
OR-99: Serves as an alternative to I-5 in some regions.
-
I-82: Connects Oregon to Washington and the Tri-Cities area, useful for inter-state freight.